Introduction — Why a Google Maps Extractor Matters
Google Maps is one of the richest sources of local business data available: millions of public listings, many with websites, phone numbers, categories, ratings and other useful metadata. For anyone doing B2B outreach, local SEO, or market research, manually collecting this data is slow and error-prone. A Google Maps Extractor automates the process so you can build clean, targeted lists in a fraction of the time.
This guide covers everything a practitioner needs to know — from the types of data you can extract and how modern extractors work, to industry-specific use cases, performance best practices, and responsible usage. We also explain how Google’s recent changes affect extraction and why Botsol’s Google Maps Scraper stays reliable through active maintenance.
What's New in 2025: Changes in Google Maps and Data Extraction
Google Maps continues to evolve in how it presents and loads listing information. A few notable changes through 2024–2025 that impact extractors:
- More dynamic content: review counts, service categories and some place details now load via background requests, requiring browser-driven extraction to capture everything.
- API field deprecations and quota limits: several Places API fields were deprecated and the free quota remains limited for large-scale lead generation.
- Shift toward browser automation: tools that run a real browser (Chrome) and parse the live UI are now the most resilient against layout changes.
- Integrated lead workflows: more tools offer built-in email finding and CRM sync — but desktop extractors still lead on raw speed and privacy for bulk jobs.
Because Google frequently makes small interface and HTML structure updates, extraction tools must adapt quickly. Botsol continuously monitors these changes and updates its Google Maps Scraper to ensure stability and accuracy. In fact, a small HTML structure change was fixed in the scraper earlier today (October 15, 2025) so users experience uninterrupted, live scraping — a detail that matters when you rely on current results for outreach.
1. Understanding Google Maps Data Structure
To extract useful leads you should understand what Google Maps exposes and where it typically appears in the UI.
- Core listing fields: business name, address, primary category, phone number, website link, opening hours.
- Metadata: place_id (internal), coordinates (lat/long), rating and reviews count.
- Supplementary fields: images, service options, price level, and short descriptions — not every listing has them.
- Links: many listings include a direct website link; extractors often follow this link to find emails or contact pages.
Modern extractors that automate a browser can collect both the visible UI fields and the dynamic data that loads after initial page render. This is important because fields like review counts and some service options are increasingly fetched asynchronously.
2. Google Maps Extractor vs. Google Maps API
There are two broad ways to get Maps data: via Google’s official APIs, or by reading the live Maps UI (extractor). Both have trade-offs:
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Google Maps / Places API | Official, documented, structured JSON, stable interface for supported fields. | Limited fields (no emails), quotas and cost for large volumes, recent deprecations for some fields. |
| Browser-based Extractor (e.g., Botsol) | Reads live UI, captures fields visible to users, can follow website links for emails, typically faster for bulk data, no per-record API cost. | Requires maintenance when Maps changes UI; desktop tools must be updated — but well-maintained tools adapt quickly. |
For lead generation where emails and deep contact data matter, many teams prefer extractors because the API rarely supplies emails and can be restrictive in quota and cost. Extractors read what an actual user would see and can follow through to the business website for additional fields.
3. What Data Can You Extract (and How Useful It Is)
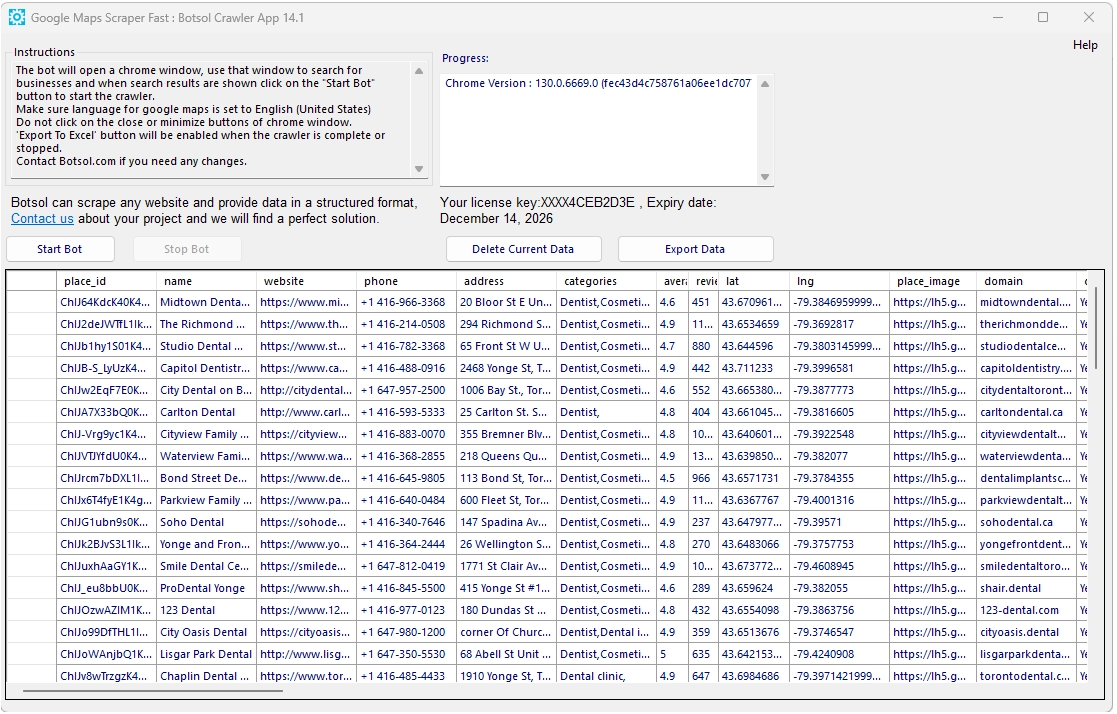
Google Maps lists an extensive range of details for each business — far beyond just the name and phone number. Botsol’s Google Maps Extractor captures this full spectrum of data fields to give you structured, ready-to-analyze information for marketing, research, or local SEO projects.
Below are some of the key fields that appear in a standard Botsol export:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| name | Business name exactly as displayed on Google Maps. |
| address | Full formatted address, broken into multiple components (adrs1–adrs7) for city, state, and ZIP segmentation. |
| phone | Primary contact number where available. |
| website | Official website link for the business. |
| Email address extracted automatically from the linked website when publicly visible. | |
| categories | Primary and secondary business categories. |
| average_rating | Average Google rating (1–5 stars). |
| review_count | Total number of Google reviews. |
| lat / lng | Latitude and longitude coordinates of the location. |
| place_id | Unique internal identifier used by Google Maps. |
| place_image | Main image or logo thumbnail from the listing. |
| claimed_google_my_business | Shows if the listing is claimed by its owner. |
| price_range | Price indicator such as $, $$, $$$ where applicable. |
| hours | Full weekly opening-hours schedule. |
| services / features | Service options, amenities, and special features provided. |
| reviews link | Direct URL to the business’s Google Reviews page. |
| booking url | Booking or appointment-link field for service-based listings. |
| social links | Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, YouTube, TikTok, Pinterest, and other detected social profiles. |
| description | Short business description or tagline from the profile. |
| plus_code | Google Plus Code (geographic shorthand for mapping coordinates). |
| url | Direct Google Maps URL of the business listing. |
The export file also includes internal tracking columns such as id, domain, scrape timestamp, and search query — useful for CRM integration or scheduled re-runs.
4. How a Modern Google Maps Extractor Works
The typical flow for a Chrome-automating extractor is:
- Accept a list of search queries or keywords + location pairs (e.g., "dentist, Sacramento" or "restaurant, 10001").
- Perform the searches in Chrome and collect the list items shown in the left panel or card view.
- Open individual listings to capture detail pages and follow the website link when present.
- Parse visible fields and export results to CSV/Excel or a database.
Unlike static scrapers, browser-based tools render JavaScript and wait for dynamic content to load, ensuring fields loaded via background requests are captured. Botsol’s scraper also supports multithreading to speed up collection while maintaining per-job control.
5. Benefits of Using a Google Maps Extractor
- Speed: Collect hundreds or thousands of listings in minutes instead of days.
- Fresh results: Extract directly from live Maps results so your lists reflect recent changes.
- Targeting: Use varied queries and geographic slices for hyper-local precision.
- Export-ready: Outputs CSV/Excel ready for CRM import and outreach sequences.
- Scalable: Desktop extractors like Botsol don’t have per-record API costs and typically impose no artificial limits on totals.
Botsol Feature Box — Why it’s a good choice
- Live scraping: The extractor scrapes from Google Maps right in front of your eyes — not from an old database.
- Very fast: Capable of extracting up to ~100 records per minute in typical scenarios.
- Chrome automation: Runs in a real browser so you have full control and can watch searches in real time.
- No limits: There’s no imposed cap on the number of businesses you can extract.
- Email extraction: Extracts emails by following business websites when emails are publicly available.
6. Industry Use Cases — Practical Examples
Different industries use Maps extraction for distinct workflows. Below are practical examples and suggested extraction patterns.
Marketing agencies
Use queries like "dentist near [city]" or "coffee shop [zip]" to build lists for outreach campaigns. Prioritize businesses with websites and multiple reviews.
Real estate & property managers
Extract businesses around a target property to compile local amenity lists or identify tenants for prospecting (restaurants, gyms, clinics).
Local service providers (plumbers, electricians)
Find potential B2B partners or unsaturated local markets by searching neighborhood-level ZIP codes and analyzing review counts and ratings.
Sales teams (B2B)
Build segmented prospect lists by industry and company size proxies (reviews, multiple locations). Combine Maps data with LinkedIn or enrichment APIs for contact persona matching.
7. How to Run a Reliable Extraction Job (Best Practices)
- Start small: Run a pilot with 3–10 queries and validate the CSV structure before a bulk run.
- Use multi-search files: Break large areas into city/ZIP-level searches to improve coverage.
- Validate samples: Always inspect 20–50 random rows from the export to ensure fields align properly.
- Throttle intelligently: Add short, randomized pauses between searches when doing very large jobs to emulate human pacing; this reduces transient UI anomalies.
- Combine enrichment: After extraction, run email verification and optional enrichment APIs to add industry tags or company size fields.
8. Performance Tips & Troubleshooting-Free Adjustments
To maximize throughput and consistency without getting into low-level troubleshooting, follow these practical tips:
- Dedicated machine: Use a dedicated Windows PC for large extraction jobs to avoid background apps interfering with browser automation.
- Network reliability: Use a stable wired or high-quality Wi-Fi connection; packet loss or intermittent connectivity can drop some dynamic data during extraction.
- Export format: Export to CSV for bulk processing; use Excel/UTF-8 options if you have non-ASCII characters in business names/addresses.
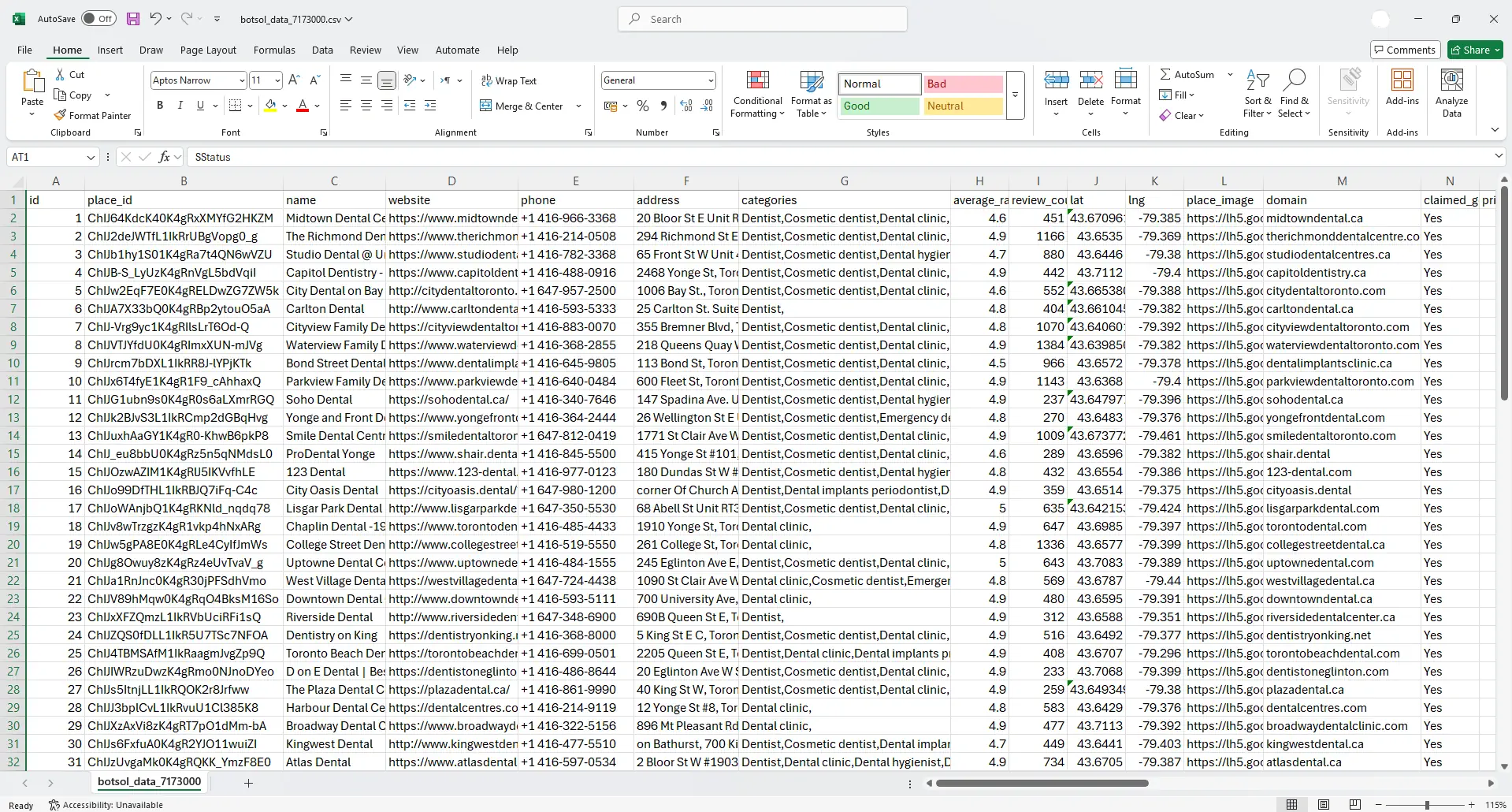
9. Exporting, Cleaning & Importing Data
Once you have your CSV/Excel file, perform the following steps before importing into a CRM:
- Normalize phone numbers: convert to international E.164 where possible.
- Deduplicate: use business name + normalized address or coordinates to remove duplicates.
- Email validation: run a validation pass to remove invalid emails or role-addresses.
- Tag sources: keep the original search query and scrape date in a column for segmentation and A/B testing of outreach.
10. Responsible Use & Compliance
Collect only publicly visible business information and follow local regulations for outreach (anti-spam laws such as CAN-SPAM, GDPR considerations for Europe, and local privacy rules). For legal guidance specific to your region or use case, consult a qualified attorney.
11. Frequently Asked Questions
- Can I extract business emails from Google Maps?
- Google Maps rarely shows emails directly. Botsol follows the website link in a listing and extracts publicly visible emails found on the business website. Where emails are present publicly, they can be included in the export.
- Is there a limit to how many businesses I can scrape?
- No — Botsol’s desktop Google Maps Extractor does not impose an artificial limit on the number of records you can collect. Large jobs may take longer but can be run in batches or overnight.
- Does the extractor work on Mac or only Windows?
- Botsol’s Google Maps Scraper is a Windows desktop application designed to automate Chrome on Windows. If you need Mac support, contact our team to discuss options.
- Should I use the Google Maps API instead of an extractor?
- If your workflow requires only the limited set of fields the API provides and you have API budget and quotas available, the Places API is a stable approach. For email discovery, full UI fidelity, and large-scale lead generation without per-record API costs, browser-based extractors remain the more practical choice.
- How often should I refresh my prospect lists?
- For active outreach lists, refresh every 3–6 months. For research or one-off campaigns, a single extraction is usually sufficient. Keep track of scrape dates in your dataset so you can prioritize recent listings.
- What do I do if a listing’s fields are missing in the export?
- First, inspect the original listing in Google Maps manually — sometimes a field is genuinely absent. If the field is visible in the browser but missing in the CSV, check the extraction settings (follow listing details, follow website links) and run a small test job to confirm.
- How accurate is Google Maps data for lead generation?
- Google Maps is generally reliable for business names, addresses and phone numbers, but the completeness of emails varies. Always validate critical contact fields before large-scale outreach to protect deliverability and reputation.
12. Appendix — Sample Job Checklist
- Define target industries and geographic scope (city/ZIP list).
- Create multi-search file with 1 query per line.
- Run a pilot extraction (3–10 queries).
- Validate sample CSV fields and clean formatting.
- Run bulk extraction in batches; export to CSV/Excel.
- Deduplicate, validate emails, and enrich as needed.
- Import into CRM and tag with source + scrape date.
Ready to collect local business leads faster?
Try Botsol Google Maps Scraper to extract live Google Maps results, follow website links for emails, and export clean CSV/Excel files.